RNA and DNA Building Blocks
Silantes offers a currently unrivaled product line for isotope labeled RNA and DNA. With many years of experience, we are a reliable source for both, isotope-labeled RNA and DNA building blocks (Nucleosides, NMPs, NDPs, NTPs and phosphoramidites and nucleobases and riboses), as well as a range of services for oligonucleotide synthesis using isotope-labeled building blocks.
Overview
Stable Isotope Labeled Nucleosides and Nucleotides as Internal Standards for Mass Spectrometry
Absolute quantification of nucleotides and nucleosides by mass spectrometry requires internal mass standards of these molecules. Silantes offers a wide range of stable isotope-labeled ribo- and deoxyribo-nucleotides and nucleosides with defined mass shifts in many modifications and combinations of the stable isotopes 2H, 13C, 15N, 19F and 18O.
Our webshop offers a selection of the most requested products. Please contact our customer service to see the complete product list or for special requests.
Learn about the Silantes production and purification technology.
Silantes Technology
Stable isotope-labelled nucleotides from Silantes are derived from bacterial DNA and RNA. The particular strain is a chemolithoautotrophic organism utilizing H2, O2 and CO2 for growth. The extracted DNA or RNA is enzymatically hydrolysed. The isolated 5’-NMPs are enzymatically phosphorylated to 5’-NDPs and 5’-NTPs and purified by IC- and RP-HPLC.

In vivo enrichment technology of biomass with stable isotopes results in:
- efficient incorporation of the stable isotopes and thus cost-effectively labelled rNTPs and dNTPs.
- high and homogeneous isotope labelling (> 98 atom %) of the nucleotides by using a closed system.
High Quality Commitment

We ensure that the isotopic enrichment exceeds >98 atom % with a chemical purity of >95 % as verified by HPLC analysis. This illustration shows an example of the HPLC elution profile of rCTP.
Moreover, the biological competence, i.e., the suitability of our rNTPs and dNTPs in enzymatic oligosyntheses, is validated by in vivo RNA and DNA syntheses, respectively.
Stable Isotope-Labeled Modified Nucleosides and Nucleotides
RNA modifications can be found in a wide range of organisms and in almost all RNA species, including tRNA, mRNA and small non-coding RNAs. These modifications are of great interest in scientific research on cellular functions related to RNA recognition, stability, and delivery. In addition, RNA based gene regulation was shown to be impacted by RNA modifications in health and disease. The determination of the stoichiometry of an RNA modification is critical since it can vary depending on the cellular stimulus like nutrition availability, stress, signal transduction, etc.
This webshop shows a selection of the most requested products. Please contact our customer service to see the complete product list or for special requests.
In the field of NTPs, all pseudouridines and N1-methylpseudouridines can be produced levels with almost any combination of labeled atoms (figure below). Note: The sugar moiety can only be labeled uniformly; the nitrogen atoms on the nucleobase can be either both labeled or both unlabeled.

The Modification You Desire with the Labeling you Require
In addition to the product examples shown in this webshop, Silantes can also synthesise custom-made molecules.
Customised modifications
Silantes can provide all bases (adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil) either as nucleoside, mono-, di-, or triphosphate and with all common modifications (e.g., methyl, pseudouridine, etc.).
Customized labeling patterns
In addition to the labeling patterns indicated in this webshop, Silantes can also realize a custom labeling pattern that is site-specific in base, ribose, or modification.
To request a quotation for the products listed or for a custom synthesis, please contact our customer service.
References
Use cases of the Silantes nucleosides and nucleotides in scientific publications:
- Spada, F., Schiffers, S., Kirchner, A., Zhang, Y., Arista, G., Kosmatchev, O., Korytiakova, E., Rahimoff, R., Ebert, C., & Carell, T. (2020). Active turnover of genomic methylcytosine in pluripotent cells. Nature Chemical Biology, 16(12), 1411–1419. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-020-0621-y
- Le, T. M., Poddar, S., Capri, J. R., Abt, E. R., Kim, W., Wei, L., Uong, N. T., Cheng, C. M., Braas, D., Nikanjam, M., Rix, P., Merkurjev, D., Zaretsky, J., Kornblum, H. I., Ribas, A., Herschman, H. R., Whitelegge, J., Faull, K. F., Donahue, T. R., . . . Radu, C. G. (2017). ATR inhibition facilitates targeting of leukemia dependence on convergent nucleotide biosynthetic pathways. Nature Communications, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00221-3
- Hagelskamp, F., Borland, K., Ammann, G., & Kaiser, S. M. (2023). Temporal resolution of NAIL-MS of tRNA, rRNA and Poly-A RNA is overcome by actinomycin D. RSC Chemical Biology, 4(5), 354–362. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2cb00243d
- Murakami, H., Horiba, R., Iwata, T., Miki, Y., Uno, B., Sakai, T., Kaneko, K., Ishihama, Y., Teshima, N., & Esaka, Y. (2018). Progress in a selective method for the determination of the acetaldehyde-derived DNA adducts by using HILIC-ESI-MS/MS. Talanta, 177, 12–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.09.055#
- Musheev, M. U., Schomacher, L., Basu, A., Han, D., Krebs, L., Scholz, C., & Niehrs, C. (2022b). Mammalian N1-adenosine PARylation is a reversible DNA modification. Nature Communications, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33731-w
- Sachse, B., Meinl, W., Sommer, Y., Glatt, H., Seidel, A., & Monien, B. H. (2014). Bioactivation of food genotoxicants 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and furfuryl alcohol by sulfotransferases from human, mouse and rat: a comparative study. Archives of Toxicology, 90(1), 137–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1392-6
- Leismann, J., Spagnuolo, M., Pradhan, M., Wacheul, L., Vu, M. A., Musheev, M., Mier, P., Andrade‐Navarro, M. A., Graille, M., Niehrs, C., Lafontaine, D. L., & Roignant, J. (2020). The 18S ribosomal RNA m 6 A methyltransferase Mettl5 is required for normal walking behavior in Drosophila. EMBO Reports, 21(7). https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201949443
- Koga, Y., Tsuchimoto, D., Hayashi, Y., Abolhassani, N., Yoneshima, Y., Sakumi, K., Nakanishi, H., Toyokuni, S., & Nakabeppu, Y. (2020). Neural stem cell–specific ITPA deficiency causes neural depolarization and epilepsy. JCI Insight, 5(22). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.140229
- McManus, J., He, T., Gavigan, J., Marchand, G., Vougier, S., Bedel, O., Ferrari, P., Arrebola, R., Gillespy, T., Gregory, R. C., Licht, S., Cheng, H., Zhang, B., & Deng, G. (2018). A Robust Multiplex Mass Spectrometric Assay for Screening Small-Molecule Inhibitors of CD73 with Diverse Inhibition Modalities. SLAS DISCOVERY, 23(3), 264–273. https://doi.org/10.1177/2472555217750386
- Stefano, J. E., Lord, D. M., Zhou, Y., Jaworski, J., Hopke, J., Travaline, T., Zhang, N., Wong, K., Lennon, A., He, T., Bric-Furlong, E., Cherrie, C., Magnay, T., Remy, E., Brondyk, W., Qiu, H., & Radošević, K. (2020). A highly potent CD73 biparatopic antibody blocks organization of the enzyme active site through dual mechanisms. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 295(52), 18379–18389. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.ra120.012395
- LC-MS based Metabolomics – DTU Findit. (n.d.). https://findit.dtu.dk/en/catalog/586bd89c6c8183835e00009a
- Niu, C., Wang, X., Gao, Y., Qiao, X., Xie, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, D., & Dong, L. (2022). Accurate quantification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA by isotope dilution mass spectrometry and providing a correction of reverse transcription efficiency in droplet digital PCR. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 414(23), 6771–6777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04238-6
- Stefano, J. E., Lord, D. M., Zhou, Y., Jaworski, J., Hopke, J., Travaline, T., Zhang, N., Wong, K., Lennon, A., He, T., Bric-Furlong, E., Cherrie, C., Magnay, T., Remy, E., Brondyk, W., Qiu, H., & Radošević, K. (2020b). A highly potent CD73 biparatopic antibody blocks organization of the enzyme active site through dual mechanisms. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 295(52), 18379–18389. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.ra120.012395
- McManus, J., He, T., Gavigan, J., Marchand, G., Vougier, S., Bedel, O., Ferrari, P., Arrebola, R., Gillespy, T., Gregory, R. C., Licht, S., Cheng, H., Zhang, B., & Deng, G. (2018b). A Robust Multiplex Mass Spectrometric Assay for Screening Small-Molecule Inhibitors of CD73 with Diverse Inhibition Modalities. SLAS DISCOVERY, 23(3), 264–273. https://doi.org/10.1177/2472555217750386
- Fromme, T., Kleigrewe, K., Dunkel, A., Retzler, A., Li, Y., Maurer, S., Fischer, N., Diezko, R., Kanzleiter, T., Hirschberg, V., Hofmann, T., & Klingenspor, M. (2018). Degradation of brown adipocyte purine nucleotides regulates uncoupling protein 1 activity. Molecular Metabolism, 8, 77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2017.12.010
- Rahbar, S., Synold, T. W., Termini, J., & Hope, C. O. (2008, August 8). US20180207116A1 – Methods of quantifying n2-(1-carboxyethyl)-2’-deoxy-guanosine (cedg) and synthesis of oligonucleotides containing cedg – Google Patents. https://patents.google.com/patent/US20180207116A1/en
- Kienhöfer, S., Musheev, M. U., Stapf, U., Helm, M., Schomacher, L., Niehrs, C., & Schäfer, A. (2015). GADD45a physically and functionally interacts with TET1. Differentiation, 90(1–3), 59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diff.2015.10.003
- Li, C., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Meng, R., Shi, X., Zhang, Y., Liang, N., Huang, H., Li, Y., Zhou, H., Xu, J., Xu, W., & Chen, H. (2023). The exotic thymidine modification 5-hydroxymethyluridine in dinoflagellateAmphidinium carterae. bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory). https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.30.569493
- Dombi, E., Marinaki, T., Spingardi, P., Millar, V., Hadjichristou, N., Carver, J., Johnston, I. G., Fratter, C., & Poulton, J. (2024). Nucleoside supplements as treatments for mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2024.1260496
-
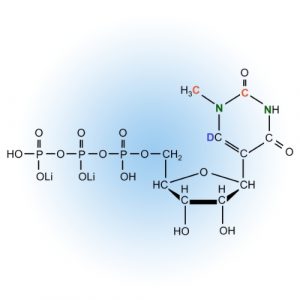
NTPs and Modifications
-
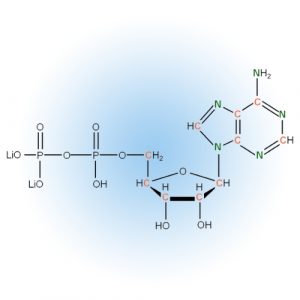
NDPs and Modifications
-
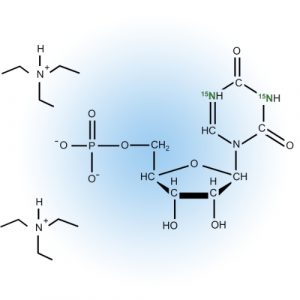
NMPs and Modifications
-
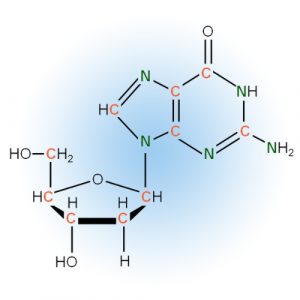
Nucleosides and Modifications
-
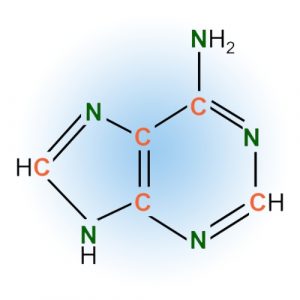
Nucleobases and Riboses
Product Categories:
Products in these categories:
-

2′-O-Methyl(D3)-Adenosine, powder
Synonym: Am-D3
1.090 € plus VAT, plus delivery Add to cart
Quantity: 5mg -

2′-O-Methyl(D3)-Cytidine, powder
Synonym: Cm-D3
1.090 € plus VAT, plus delivery Add to cart
Quantity: 5mg -

2′-O-Methyl(D3)-Guanosine, powder
Synonym: Gm-D3
1.090 € plus VAT, plus delivery Add to cart
Quantity: 5mg -

2′-O-Methyl(D3)-Uridine, powder
Synonym: Um-D3
1.090 € plus VAT, plus delivery Add to cart
Quantity: 5mg -

5-Methyl(D3)-Cytidine, powder
Synonym: m5(D3)rCyd
1.090 € plus VAT, plus delivery Add to cart
Quantity: 5mg -

N1-Methyl(D3)-Adenosine powder
Synonym: m1A-D3
1.150 € plus VAT, plus delivery Add to cart
Quantity: 5mg
